If you are unsure about which country would be suited for your studies, allow us to pique your interest in Canada, known for its high quality of life and prestigious universities. Read our guide below to find out everything you need to know about what studying in Canada means.

A Quick Intro to Canada
Why Study in Canada?
Higher Education in Canada
Higher Education Institutions in Canada
Pathway to Studying in Canada
Top Institutions in Canada
After Study Opportunities in Canada
Applying to Study in Canada
Language Requirements
Visa Requirements
Tuition Fees
A Quick Intro to Canada

Continuously emerging in the list of the top ten countries with the highest quality of life in the world, Canada is also the second most educated country in the world, where more than half of its residents possess a college degree and education is compulsory until the age of 16 to 18 years. Hence, Canada is a major competitor in the industry of higher education.
Canada is known for its winters, and in several areas of the country, the ground is covered with snow for the stretch of half a year. Fret not, though – universities tend not to be located in such areas. The cool winters, coupled with the country’s 561 lakes and largest coastline in the world, mountains and lush greenery, students would gain an enriching outdoor experience while studying in Canada.
Why Study in Canada?

Studying in Canada will give you a life experience not to forget! You will find enriching discoveries in a culture that is both unique and different. You may have heard of the kindness and generosity of Canadians in general, and that is no exaggeration, as you will experience once you settle down in the country. In fact, because of these qualities, the United Nations consistently ranks Canada as one of the best places in the world to live in. Canada puts a high value on human rights, equality, and a stable and peaceful society. Also, it is too exceptionally multi-cultural, with much of its population relying on immigrants. Fitting in, so to say, will not be an issue for potential students who wish to study in Canada!
Moreover, English and French are Canada’s national languages, so as long as you are proficient in one of these two languages, a language barrier would not be a problem while studying in Canada.
And very important, Canada offers a high-quality education. Many universities and colleges in Canada are recognised in the rankings worldwide. The degree you obtain at a university or college in Canada is also acknowledged globally, so studying in Canada will most definitely boost your curriculum as well as your chances of getting a good job in or outside Canada.
Higher Education in Canada
As of 2015, Canada is the eighth most popular country for international students. According to UNESCO, the country has 120,960 international students. It’s not impossible to see Canadian cities’ appeal as each region in Canada offers a distinctive living and studying experience. For example, Montreal, where Canada’s top university McGill University is located, is known to be the country’s “cultural capital.” It was also recently named, as the Best City for Students. Toronto, home of the University of Toronto, is the country’s largest city and known as one of the most multicultural cities in the world. Those who like the idea of living the city life with easy access to the great outdoors will find Vancouver, and one of its universities – University of British Columbia, an excellent choice.
A. Higher Education Institutions in Canada
Today, Canada has about 163 recognised public and private institutions, including theological schools, plus 183 recognised public colleges and institutes, which includes those who grant applied and bachelor’s degree. Further, there are 68 university-level institutions and 51 college-level ones operating as authorised institutions, at which only selected programs are approved under provincially established quality assurance programs., according to Council of Ministers of Education, Canada (CMEC).
The higher education system in Canada differs in each province. This means each province and territory mandates and funds their institutions, and they have their regulations (which they strictly follow) as there is no federal accreditation. With this, credentials might differ in each province as well.
Universities
| Public | Private |
|---|---|
|
Receives funding from provincial, territorial and/or federal government, but they also charge for tuition fees and can accept private funding. Managed by a body appointed or elected, and are properly evaluated by public authorities. |
Does not receive funding from the provincial, territorial and/or federal governments, as funding comes from alumni donations, grants, and tuition fees. They use this to acquire resources for their students and faculty. |
Some universities in Canada are also members of the U15 Group of Canadian Research Universities (U15). This group of universities is known as Canada’s leading research-intensive universities, undertake 80% of all competitive university research in Canada. The member universities are:
- University of Alberta
- University of British Columbia
- University of Calgary
- Dalhousie University
- Université Laval
- University of Manitoba
- McGill University
- McMaster University
- Université de Montréal
- University of Ottawa
- Queen's University
- University of Saskatchewan
- University of Toronto
- University of Waterloo
- University of Western Ontario
Colleges
These schools refer to technical, applied arts, or applied science school. These institutes can grant certificates, diplomas, associate degrees, and bachelor’s degree.
However, in Quebec, people refer to it as CEGEP (originally a French acronym for Collège d'enseignement général et professionnel). It is the public post-secondary education collegiate institutions where students can take either a 2-year pre- or 3-year post-programme before they can pursue an undergraduate degree at a university.
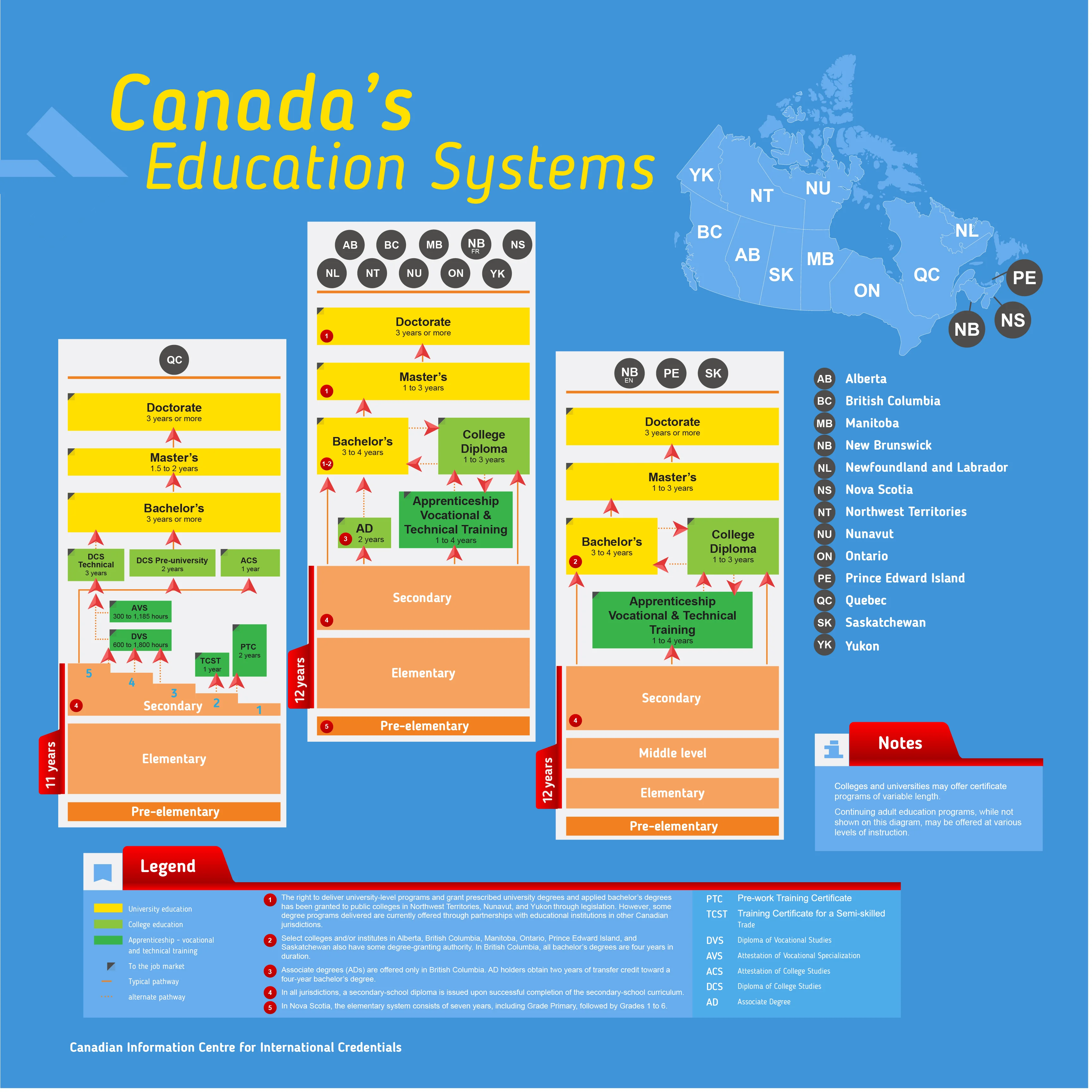
B. Pathway to Studying in Canada
The length of your study depends on the path you wish to take. Here’s a basic duration of study in Canada

C. Top Institutions in Canada
There are 26 Canadian universities present in the QS World University Rankings 2021, which alone shows the high standard of education in Canada.

D. After Study Opportunities in Canada
Still not homesick and you feel like staying in Canada longer? We feel you! And Canada understands you as well because now you have the opportunity to stay longer in Canada after your studies!
If you are planning to work after your study in Canada, then you should apply for a Post-graduation work permit which can be issued for a maximum of three years.
If you are planning to stay in Canada for any other reason, please check out the government website for application and requirements.
Applying to Study in Canada

A. Language Requirements
The most general admission requirement to be eligible for applying to Canadian universities include a high school diploma, and proof of your English or French language proficiency, which can be presented through your O-Level English grade, the IELTS, or the TOEFL grades.
B. Visa Requirements
If your course of study will last more than six months, obtaining a student permit must be done to study in Canada, in which several documents and forms are required from the student. Student permits can be attained online at the Citizenship and Immigration Canada (CIC) website or through a paper application, though the latter would take double the time as the former. However, to be applicable to the online process, you would first be required to answer a few questions on the CIC website, after which you would receive a personal checklist code for the duration of your application process. Create a MyCIC account, and proceed to apply for your student permit.
Once students are offered a placement at a university in Canada, the visa application process can begin by submitting the following documents:
- Acceptance letter from your university of choice, which must be a recognised university
- Prior academic record
- Proof of English language proficiency
- Bank statement for proof of financial stability for annual tuition fee, living costs and return transport
- Non-existent criminal record
- Biometrics for students from certain countries
- Medical exam report
- Two passport-sized pictures
Once you obtain visa approval, you will receive a letter of introduction or an Electronic Travel Authorisation (eTA). Upon arrival in Canada, you must present your passport, financial proof and letter of acceptance to Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) for your student permit and entry into the country.
Tuition Fees
Tuition fees are also very competitive when compared with other top study destinations for international students. According to a recent study by HSBC, Canada is more affordable than in countries such as Australia, the US and the UK. For international students who need financial assistance, the Canadian government, universities and other organisations have a line-up of scholarships.
| Study Level | Tuition Fee, Per Year, in CAD | Tuition Fee, Per Year, in USD |
|---|---|---|
| Bachelor's Degree | Between 14,000 - 51,000 | 10,500 - 38,250 |
| Master's Degree | Between 12,000 - 44,800 | 9,000 - 33,500 |
| Doctorate's Degree | Between 15,000 - 30,000 | 11,400- 22,600 |
Want to know more about studying in Canada? Check out our other articles, below:
- Cost of living in Canada
- Why study in Canada?
- Economic outlay of Canada
- Salary outlay in Canada
- Who studies in Canada?
- Lifestyle in Canada
 +60173309581
+60173309581